

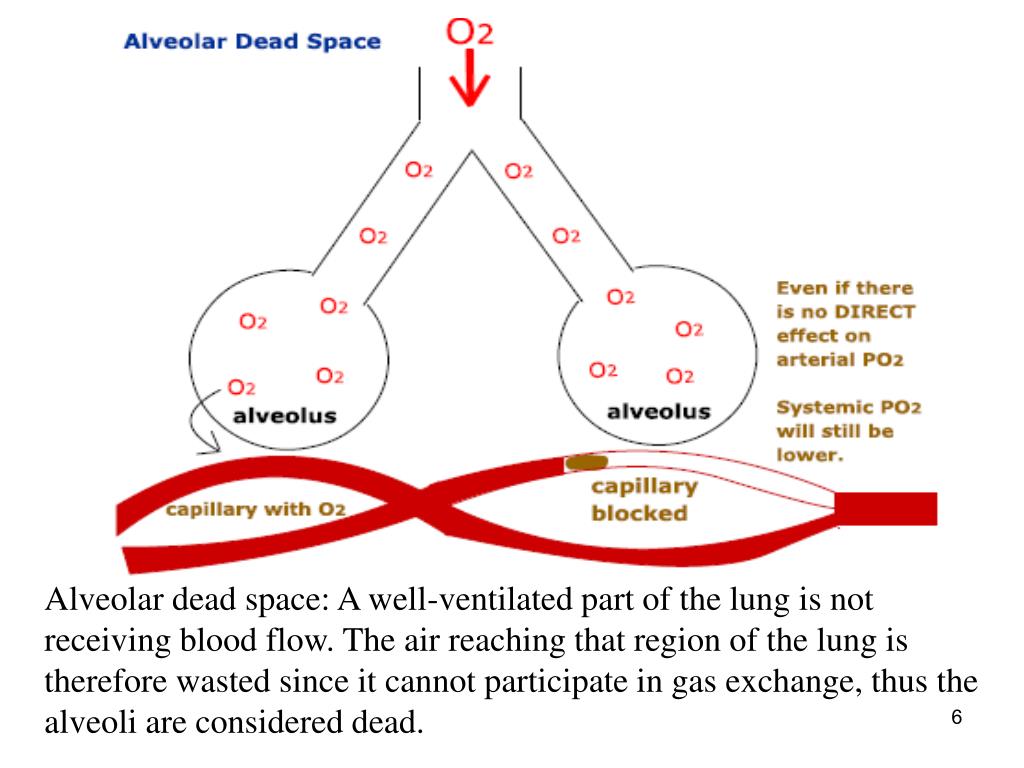
Pa-E'CO(2)/PaCO(2) may be a useful serial measurement in the critically ill patient because all the necessary data are easily obtained and calculation is significantly simpler than for (VDalv/VTalv)(Bohr-Fowler). Induced variation was slightly larger for Pa-E'CO(2)/PaCO(2) during changes in VDanat, but was similar during variation of venous admixture and Vdot CO(2). During constant alveolar configuration, the factors examined (Vdot CO(2), pulmonary shunt fraction, and VDanat) each caused variation in (VDalv/VTalv)(Bohr-Fowler) and in Pa-E'CO(2)/PaCO(2). Pa-E'CO(2)/PaCO(2) was approximately 59.5% of (VDalv/VTalv)(Bohr-Fowler). We examined the variability of Pa-E'CO(2)/PaCO(2) and of (VDalv/VTalv)(Bohr-Fowler) in the presence of three ventilation-perfusion defects while varying CO(2) production (Vdot CO(2)), venous admixture, and anatomical dead space fraction (VDanat). Using an original, validated, high-fidelity model of pulmonary physiology, we compared the arterial to end-tidal CO(2) gradient divided by the arterial CO(2) tension (Pa-E'CO(2)/PaCO(2)) with alveolar dead space expressed as a fraction of alveolar tidal volume, calculated in the conventional manner using Fowler's technique and the Bohr equation: (VDalv/VTalv)(Bohr-Fowler).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
